
Head over to our on-demand library to view sessions from VB Transform 2023. Register Here
This article is part of a VB special issue. Read the full series here: The future of the data center: Handling greater and greater demands.
Zero trust is the virtual shield data centers need to harden against increasingly complex, well-orchestrated data center attacks. Attackers are gaining access to data centers using stolen privileged access credentials and IDs, looking to exfiltrate as much customer data as possible.
Just to name two examples, attackers successfully obtained emails, passwords and other customer data from Shanghai-based GDS Holdings Ltd. and Singapore-based ST Telemedia Global Data Centres, two of Asia’s largest data center operators.
Resecurity Inc. recently provided an in-depth analysis of attackers’ strategies to infiltrate data centers, cloud service providers and managed service providers. Resecurity found that the most vulnerable threat vectors for data centers include customer support, customer service, and ticket management support portals running on data center servers. Attackers can gain enough control to steal thousands of customer records and exfiltrate a company’s most confidential data if not discovered.
Event
VB Transform 2023 On-Demand
Did you miss a session from VB Transform 2023? Register to access the on-demand library for all of our featured sessions.
The challenge for CIOs and CISOs is to deliver virtual shields that scale
Designing for trust must start with the cornerstone of zero trust: the belief that the data center has already been breached, and further damage must be contained and stopped immediately. That’s because attackers are continuously fine-tuning their craft to find and exploit gaps in data center security architectures and tech stacks. These gaps often appear when long-standing on-premise security platforms are extended to the cloud without the correct configurations, leaving the systems vulnerable to breach.
CIOs and CISOs are teaming up to tackle the challenge of fast-tracking secure access service edge (SASE) and zero trust network access (ZTNA) initiatives in data centers to harden virtual shields against further attacks. CIOs tells VentureBeat that SASE improves enterprise security postures by providing ZTNA at scale while helping to consolidate data center and enterprise-wide security.
ZTNA needs to be on every CISO’s SASE roadmap. Gartner predicts ZTNA will be the fastest-growing network security market segment worldwide. It’s forecast to achieve a 27.5% compound annual growth rate between 2021 and 2026, increasing from $633 million to $2.1 billion worldwide.
Esmond Kane, CISO of Steward Health, advises, “Understand that — at its core — SASE is zero trust. We’re talking about identity, authentication, access control and privilege. Start there and then build out.”
CIOs and CISOs are seeing their roles overlap in cybersecurity, making shared ownership of data center security outcomes a must. At 19% of publicly-traded companies and 46% of private companies, the CISO currently has the double role of CISO and CIO, according to a survey of 650 security executives published earlier this year by Hitch Partners.
CIOs tell VentureBeat that their boards of directors consider getting data center security right to be integral to their risk management. Eighty-eight percent of boards now view cybersecurity as a business risk. Foundry’s State of the CIO Study 2023 found that security improvements are the most significant factor driving tech budget increases in 2023.

Top 10 cybersecurity priorities for 2023
There’s no shortage of cybersecurity weaknesses known to attackers, who seek to exploit them undetected. From the unsecured networks connecting data centers across an organization to the legacy systems relying on perimeter-based security, many data centers are breaches waiting to happen. Moving workloads to the cloud often expands the attack surface, with hybrid multicloud platforms among the riskiest and most challenging to secure. Enterprises getting the best results base their data center cybersecurity strategies on proven frameworks, with SASE and ZTNA the most prevalent.
1. Prioritize identity security first, using single sign-on (SSO) and multifactor authentication (MFA)
“The best place to start is always around enforcing multifactor authentication,” Forrester senior analyst Andrew Hewitt told VentureBeat. Hewitt is the author of the report, The Future of Endpoint Management. “This can go a long way toward ensuring that enterprise data is safe. From there, it’s enrolling devices and maintaining a solid compliance standard with the unified endpoint management (UEM) tool,” he added.
2. Make auditing access privileges, deleting obsolete accounts and reviewing admin rights part of the organization’s muscle memory
According to Ivanti’s 2023 Cybersecurity Status Report, 45% of enterprises believe former employees and contractors still have active access to company systems and files due to inconsistent or nonexistent procedures for canceling access. De-provisioning is rarely done, and third-party apps still have access. “Large organizations often fail to account for the huge ecosystem of apps, platforms and third-party services that grant access well past an employee’s termination,” said Srinivas Mukkamala, chief product officer at Ivanti.
Leading IAM providers include AWS Identity and Access Management, CrowdStrike, Delinea, Ericom, ForgeRock, Ivanti, Google Cloud Identity, IBM Cloud Identity, Microsoft Azure Active Directory, Palo Alto Networks and Zscaler.
3. Consider replacing legacy IAM systems that can’t monitor identities, roles and privileged access credential activity early in your SASE and ZTNA roadmaps
VentureBeat has learned from CISOs that legacy IAM systems long used to protect networks and data centers are having trouble keeping up with the vast numbers of new identities being generated today. An IAM that can track only some identity activity across roles, privileged access credential use, and endpoint used in real time is too risky. Legacy IAM systems have gaps that attackers exploit by offering bounties on the dark web for privileged credentials to financial services’ central accounting and finance systems, for example.
4. Microsegmentation can reduce data center lateral movement and attack surfaces when a breach happens
Succeeding with an SASE framework supported by ZTNA needs to start with the assumption that the data center has already been breached. The goal is to stop lateral movement immediately and reduce the threat of attack surfaces leading to a breach.
The NIST zero-trust framework prioritizes microsegmentation alongside identity-based governance, authentication, and network and endpoint security management. Airgap Networks, AlgoSec, ColorTokens, Illumio, Prisma Cloud and Zscaler Cloud Platform use microsegmentation to detect and stop intrusions and breach attempts early.
One of the most innovative is AirGap Networks, one of the top 20 zero-trust startups to watch in 2023, which introduced its Airgap Zero Trust Firewall, or ZTFW, earlier this year. ZTFW prevents threats from spreading from IT to the core network and vice versa, even if higher network layers have been compromised. Airgap’s ZTFW defends critical business infrastructure and secures core networks by providing identity, agentless microsegmentation, and secure access for every connected endpoint.
Last month AirGap Networks acquired NetSpyGlass to enable Airgap ZTFW customers to better detect, locate and contain device anomalies in real time. “The greater the accuracy of asset discovery in these systems, the shorter the response time,” said Ritesh Agrawal, CEO and cofounder of Airgap Networks. “With the addition of NetSpyGlass, the Airgap ZTFW offers businesses the steering wheel to drive trust [in] their core network at speed and scale. It’s a game-changer for securing business-critical networks.”
5. Real-time asset management across all endpoints and data centers is table stakes
CISOs use IT asset management systems and platforms to find and identify network equipment, endpoints, related assets, and contracts. Combining bot-based asset discovery with AI and ML algorithms improves IT asset management accuracy and monitoring.
Ivanti’s Neurons for Discovery combines bot-based asset discovery, AI and ML to create real-time service maps of network segments or an entire infrastructure. In addition, Ivanti updates configuration and asset management databases to receive real-time normalized hardware and software inventory and usage data. Other leading asset management providers include Absolute Software, Airgap Networks, Atlassian, CrowdStrike, BMC, ManageEngine, MicroFocus and ServiceNow.
6. Real-time telemetry data can extend endpoint lifecycles and catch intrusion attempts that might otherwise be missed
Endpoint security requires real-time endpoint telemetry data to detect intrusions and breaches. This data is also helpful in identifying every endpoint’s hardware and software configuration at every level — file, process, registry, network connection and device data. Absolute Software, BitDefender, CrowdStrike, Cisco, Ivanti and Microsoft Defender for Endpoint, which secures endpoint data in Microsoft Azure, and other leading vendors use real-time telemetry data to generate endpoint analytics.
CrowdStrike, ThreatConnect, Deep Instinct and Orca Security calculate IOAs and IOCs using real-time telemetry. IOAs identify an attacker’s intent and goals regardless of malware or exploit. IOAs and IOCs provide forensics to prove a network breach. Automating IOAs gives accurate, real-time data to understand attackers’ intent and stop intrusion attempts.
CrowdStrike launched the first AI-powered IOAs to protect endpoints using real-time telemetry data. The company told VentureBeat in a recent briefing that AI-powered IOAs work asynchronously with sensor-based machine learning and other sensor defense layers.
7. As data center endpoints take on more identities, they need audits and improvements to crucial digital certificate management
Each network machine needs a unique identity to manage and secure machine-to-machine communications. More identities on endpoints make it harder to secure them all.
Key and digital certificate management must be prioritized. SSL, SSH keys, code-signing certificates, TLS, and authentication tokens assign digital identities. Cyberattackers bypass code-signed certificates or compromise SSL and TLS certificates to attack SSH keys. Data center security teams must ensure that every machine’s identity is accurate, reliable and trustworthy. CheckPoint, Delinea, Fortinet, IBM Security, Ivanti, Keyfactor, Microsoft Security, Venafi and Zscaler are leading providers in this area.
8. Datacenter endpoints must identify an intrusion attempt and autonomously self-heal
CISOs tell VentureBeat they are inheriting data centers located five or more time zones away. Sending staff to refresh endpoints isn’t feasible or financially prudent given the budget crunch many face. Many are evaluating and adopting self-healing endpoints that can capture and act on real-time telemetry data, rebuild themselves if breached, and can be programmed to brick themselves if necessary.
Closing the gaps between identity management and endpoint security is the future of zero trust. Michael Sentonas, CrowdStrike’s president, told VentureBeat in a recent interview that closing the gap between identities and endpoints is “one of the biggest challenges that people want to grapple with today. I mean, the hacking [demo] session that George and I did at RSA [2023] was to show some of the challenges with identity and the complexity. The reason why we connected the endpoint with identity and the data that the user is accessing is because it’s a critical problem. And if you can solve that, you can solve a big part of the cyber problem that an organization has.”
Absolute Software, Akamai, Cisco, CrowdStrike, ESET, Cybereason Defense Platform, Ivanti, Malwarebytes, Microsoft, SentinelOne, Tanium, Trend Micro and many others vendors offer autonomously self-healing endpoints. Absolute Software is among the most unique in that it provides an undeletable digital tether to every PC-based endpoint to monitor and validate real-time data requests and transactions. Absolute’s Resilience platform automatically repairs or reinstalls mission-critical applications and remote queries, remediating remote devices at scale. The platform can also discover sensitive data on endpoints and investigate and recover stolen devices. Absolute also turned its endpoint expertise into the industry’s first self-healing zero-trust platform.
9. Deploy risk-based conditional access for every data center threat surface, starting with endpoints
Risk-based access for applications, endpoints and systems is enabled in least-privileged access sessions based on device type, settings, location and anomalous behaviors. Real-time risk scores are calculated by cybersecurity vendors using ML algorithms. “This ensures MFA (multifactor authentication) is triggered only when risk levels change — ensuring protection without loss of user productivity,” CrowdStrike’s Raina told VentureBeat. Leading vendors providing risk-based conditional access include CheckPoint, CrowdStrike, Fortinet, IBM Security, Ivanti, Microsoft Security, Venafi and Zscaler.
10. Data-driven, automated patch management reduces IT team workload
CIOs tell VentureBeat that their IT teams are too overwhelmed with projects and urgent requests to work through the inventory of devices that need updates. A data-driven approach is needed for large-scale patch management.
Leading banking, financial services and manufacturing companies, and CIOs and CISOs who run multiple data centers, are adopting AI- and ML-based systems to keep the thousands of devices across their data centers updated. Leading vendors include Broadcom, CrowdStrike, Ivanti, SentinelOne, McAfee, Sophos, Trend Micro, VMWare Carbon Black and Cybereason.
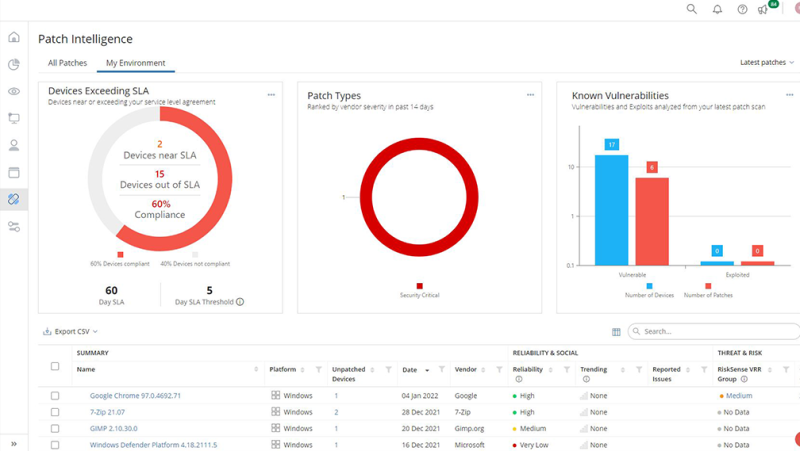
Ivanti’s Neurons platform uses AI-based bots to find, identify and update all endpoint patches. Ivanti’s risk-based cloud patch management integrates the company’s vulnerability risk rating (VRR) to help SOC analysts prioritize risk. Ivanti discovered how to track service-level agreements (SLAs) and alert teams to devices nearing SLAs.
Data center cybersecurity is a business decision
CIOs and CISOs need to partner to define a unified cybersecurity strategy to protect data centers, many of which are being protected with legacy perimeter-based systems today. Choosing an SASE-based strategy with ZTNA at its core is the direction many banking, insurance and financial services enterprises are going today. This approach is well suited for financial services, for example, which must keep certain systems on-premises for compliance requirements.
Attackers move faster than the most efficient IT, cybersecurity and SecOps teams do today. To protect their data centers, CIOs, CISOs and their teams must start by protecting identities first. The 10 priorities above are a roadmap to get started creating a hardened virtual shield that will reduce breaches and alleviate their severity. Breaches are coming; it’s a matter of minimizing the blast radius and reducing the losses they’ll create.
VentureBeat’s mission is to be a digital town square for technical decision-makers to gain knowledge about transformative enterprise technology and transact. Discover our Briefings.






